Yeats' View of History
Different cultures have different notions of the shape of history. Yeats' own personal myth of history borrows from several different models:
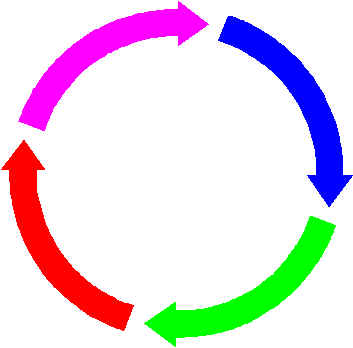
The Ancient Attic Greek (as well as the classic Chinese and ancient Semitic) notion of history is one that is essentially circular. History is conceived as either essentially static, moving through a yearly cycle, or cyclical in the sense of a "Great year" a centuries-old cycle where various ages of humanity eventually repeat older patterns; thus, the "golden" age is followed by the "silver," "bronze," and "lead". This is eventually followed by a new golden age, etc.
The Modern Enlightenment notion of history from the seventeenth through the nineteenth century was one of essential progress. History is moving in a singular direction, increasingly improving in matters of knowledge, science, lifestyle, freedom, etc.
Christianity's view of history can be thought of as a spiral. It recognizes that human beings tend to replicate the mistakes of the past and that humans continue to be fallen beings, yet it also recognizes that history has a direction and a final end. God has promised to return and renew all things.
Naturalistic evolutionary theory is often associated with the Enlightenment view of history, but strictly speaking, it does not judge whether something is good or evil; rather, it understands history to be a wave: things change and they move in a certain direction, but this is not necessarily for the better. It simply is.
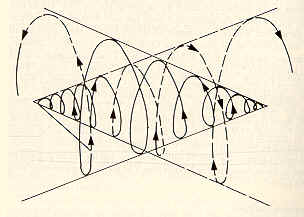
Yeats conceptualized history as a series of interpenetrating gyres. Historical eras overlap, one ending as the next one begins. He believed that these gyres or eras of history tended to fall into roughly 2,000-year periods. While one tends to dominant, the other is always implied and weakly present. He believed that a new "rough beast" was coming to replace Christianity and that the ideal time to live would be when the two gyres were at the midpoint of change. He believed that Byzantium in the year 1000 A.D. represented this ideal time.